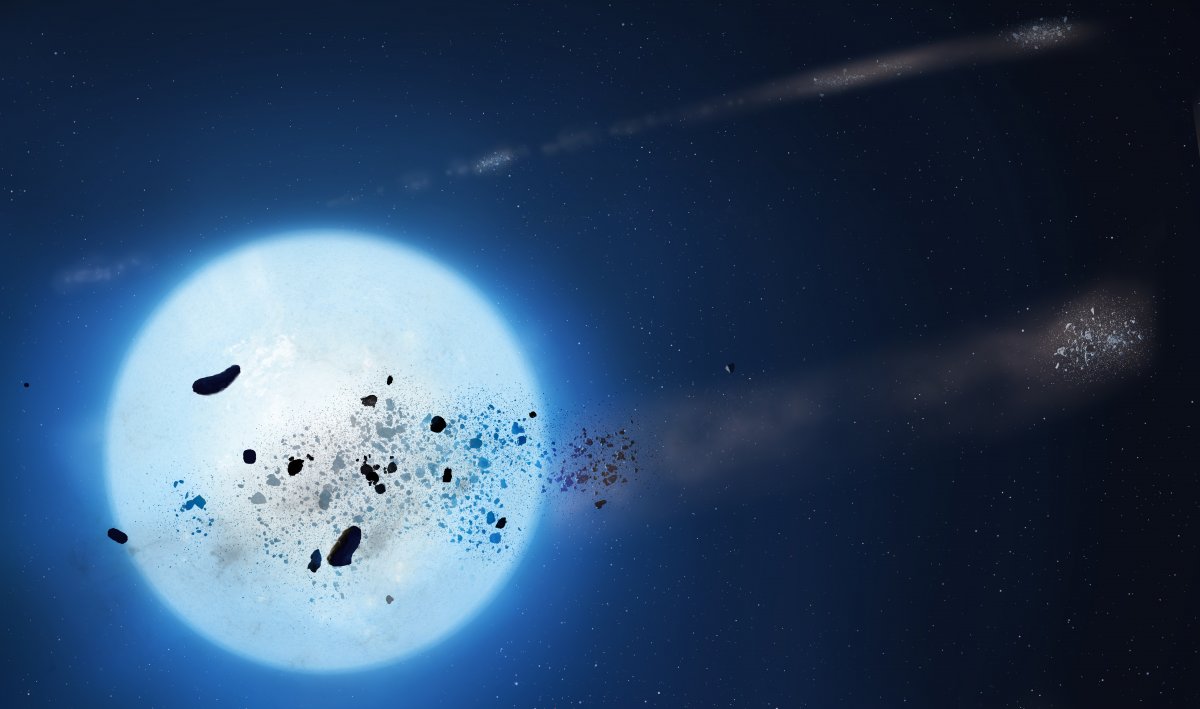
When the Sun expands into a red giant at the end of its life, it may engulf not only Mercury and Venus, but Earth as well. But even if our homeland escapes this fate, once the Sun becomes a white dwarf star, it will lose its atmosphere and all oceans and “will no longer be a friendly place to live.” At least that's how a research group from Great Britain summarizes the current state of research in a paper on the fate of planets, asteroids and moons in such a star system. What is happening to these celestial bodies is quite “monstrous and catastrophic,” and is happening simultaneously over relatively short time periods from an astronomical perspective. The team was able to confirm this using several white dwarf stars.
advertisement
Pre-slicing planetary system
As the team summarizesObjects in white dwarf stars are torn apart by immense gravity until they break apart into smaller and smaller pieces. Collisions eventually cause it to decay into dust that falls into the stars. When this happens, astronomers can analyze their composition based on the changing light they emit. The group did this and at the same time summarized how such evolution could occur in the solar system. Thus the fate of the Earth is not certain; Our home planet may or may not survive the expansion of the Sun. What's left of the Earth could orbit what's left of the Sun. Things are certainly different not only for the two innermost planets, but also for many of Jupiter's and Saturn's moons. They could undergo the dismemberment process the group was looking for.
The team studied the processes in three white dwarf stars in more detail, which at first glance appear very different. One of them acts very calm and “well-behaved”, but there is a reference to a catastrophic event that occurred 14 years ago, when a celestial body there was likely destroyed. Others become darker every few months, with violent fluctuations in brightness. This should indicate which parts revolve around it. Another shows very different darkening stages that are interpreted similarly. Research work This is now presented in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, but the team explains that some of the transits or dimming phases examined have already disappeared again. This confirms how messy things are in the systems. We still have about five billion years until this happens in our solar system.
(meh)

“Tv expert. Hardcore creator. Extreme music fan. Lifelong twitter geek. Certified travel enthusiast. Baconaholic. Pop culture nerd. Reader. Freelance student.”






More Stories
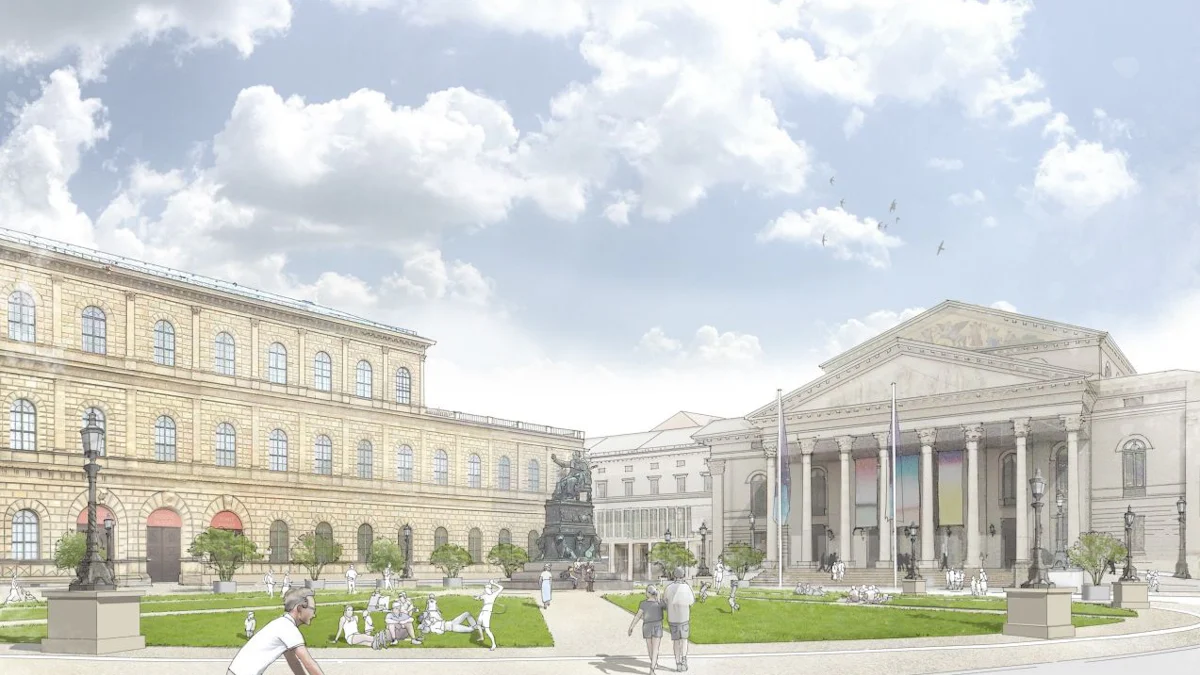
Temporary solution for Max Joseph Platz: Green Center in front of the Opera – Munich
The square in front of the Opera House in Munich: this is how Max Joseph Platz is rebuilt
“Spiders on Mars” – Here's What's Behind It – News